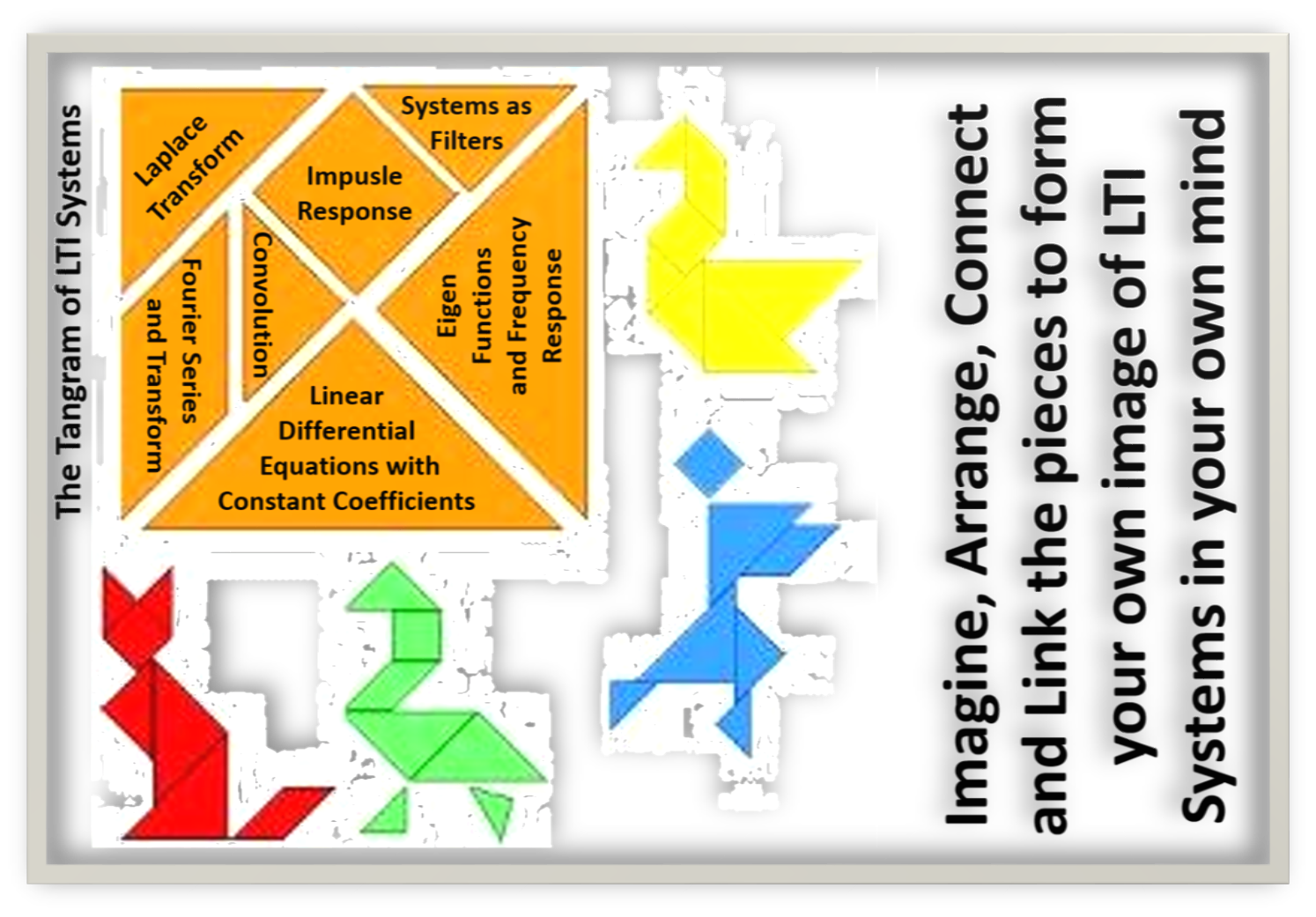
| Topics | Notes | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singularity (Step, impulse, ramp) functions | |||
| Solution of a linear differential equation | |||
| System Properties (Linearity, Time invariance, Memory, Causality, Invertibility) | Linear, Time invariant System: how to check? | ||
| Convolution and circuit response | |||
| Fourier Series | Handout | ||
| Fourier Transform | Handout | ||
| Laplace Transform and Circuit Elements | Circuit elements: a deeper look Circuit analysis with Laplace tranform |
||
| Discrete time signal | Linear difference equations - Part - I Linear difference equations - Part II |
| Chapters | #Hours | Notes (Notes + Class discussions = Exam Syllabus) |
Videos (Videos != Exam syllabus) |
Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Network theorems | 3 classes | Suggested reading: Hayt: Section 15.1, 15.2, 15.3; Alexander: Section 15.5 Practice Problems: Hayt: Exercise 15.1, 15.2, 15.3; Alexander: Section 15.5 Nano Project 1, 2 and 3(Theoratical and optional): see below |
||
| 2 | Magnetically coupled circuits | 3 classes |
|
Nano Project 4 | |
| 3 | Network analysis with graph theory | 3 | |||
| Autumn Break | |||||
| 4 | Two port networks | 1 | After reading the notes, open the index page of D Roy Choudhury. Glance through the topic names listed in the index. There are quite a few additional topics. Guess what those could be just from the names/titles. If you can guess, you don't have to read it. If you feel curious about any topic, you may read. Nano Project 4 (see below) | ||
| 5 | Frequency response: Analysis and synthesis (briefly) | 3 | All notes not available yet |
|
Play and have fun with this filter applet |
| The End |
| J | Monday 2:00PM - 5:00PM | Dual Deg CS, QDE |
|---|---|---|
| X | Wednesday 2:00PM - 5:00PM | Dual Deg EE, IE |
| N | Thursday 2:00PM - 5:00PM | EE 4th Year |
| P | Friday 2:00PM - 5:00PM | CS 4th Year |
| 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Transient and frequency response of R-L-C series circuit | Derivation of transient response by solving a differential equation Part 1 (I may change it to make it similar to the way TKB sir taught in the class),Intro to frequency response (will be improved soon) |
| 3 | Active lowpass filter | Opamp fundamentals (Explanations updated) |
| 4 | Fourier Coefficients of a Periodic Signal | |
| 5 | 2 Port Network | |
| 6 | 1 Port network | Opamp fundamentals The philosophy of negative impedance Active negative impedance circuit with an opamp Positive and Negative Feedback |
